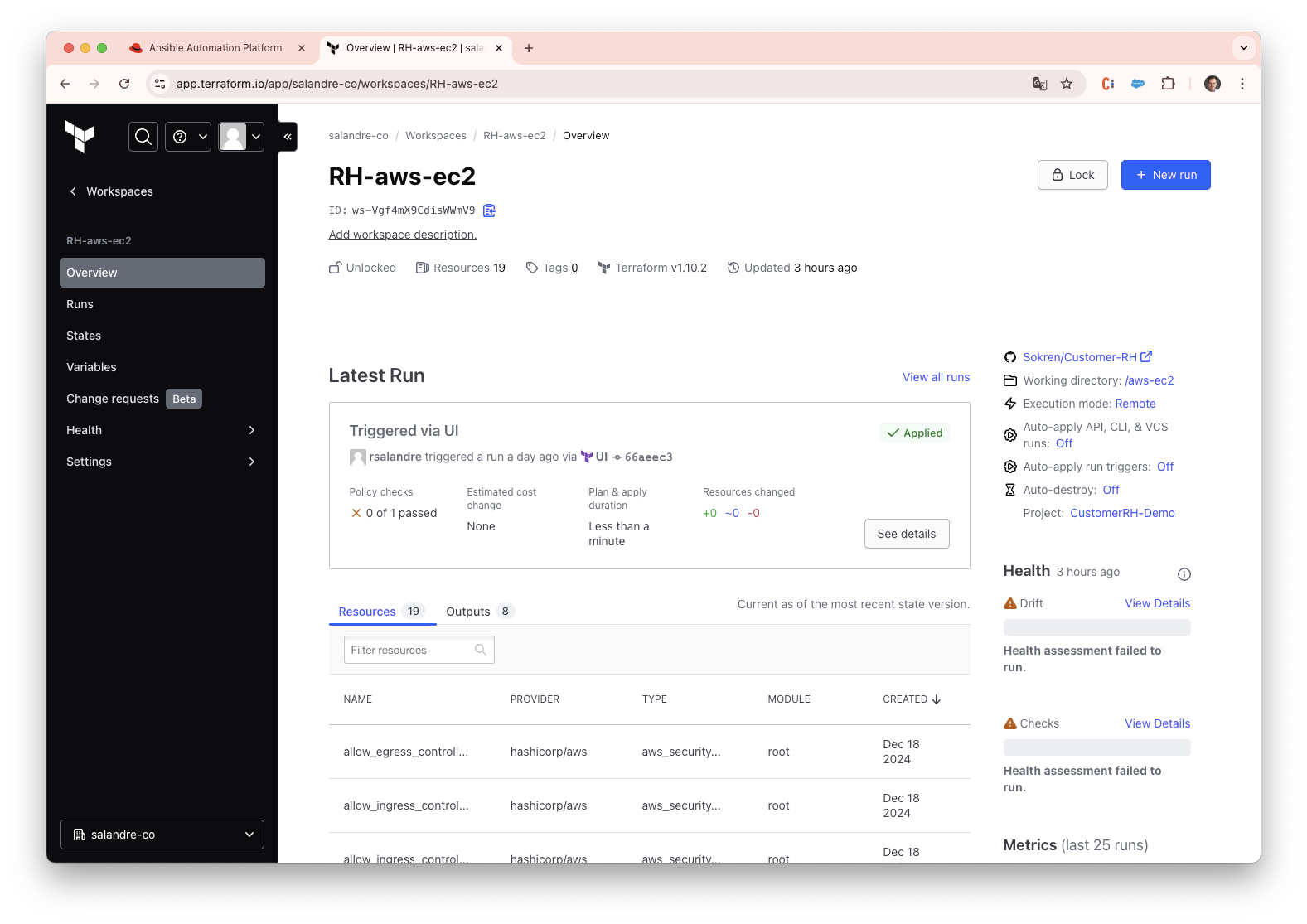
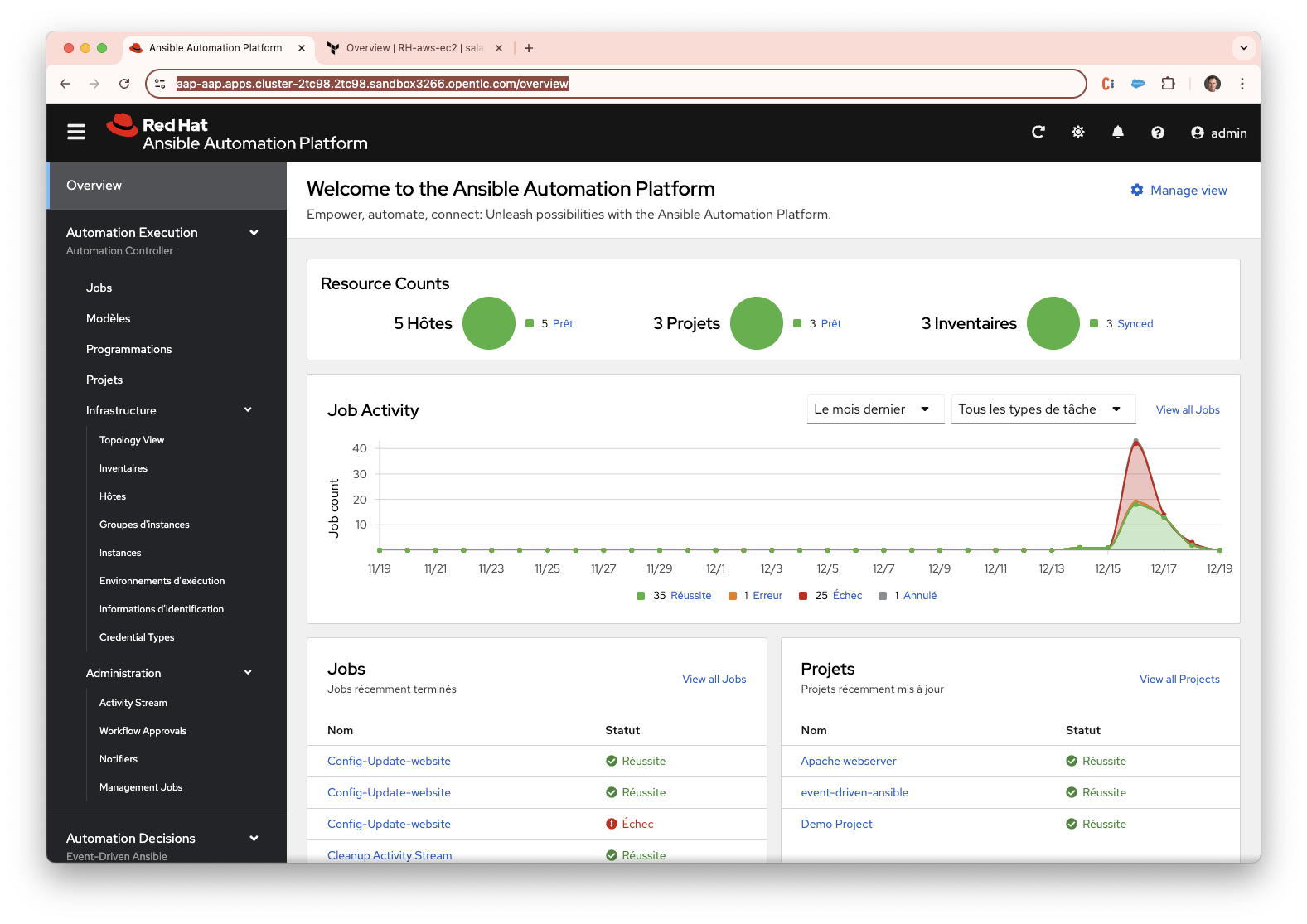
As IT environments shift from traditional on-premise data centers to multi-cloud ecosystems, organizations need scalable, secure, and efficient solutions for Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
By leveraging Red Hat’s Ansible Automation Platform and HashiCorp’s Terraform Enterprise, organizations can unlock new levels of automation and governance across hybrid and multi-cloud resources.

The Power of Integration
The Ansible Automation Platform excels in application deployment and configuration management, while Terraform Enterprise is the go-to solution for infrastructure provisioning at scale.
Together, they enable:
- Provisioning Infrastructure: Terraform Enterprise allows for the provisioning of scalable and secure IaaS or PaaS resources.
- Configuring and Enforcing Compliance: Ansible Automation Platform finalizes infrastructure configurations, applies policies, and enforces them to meet organizational standards.
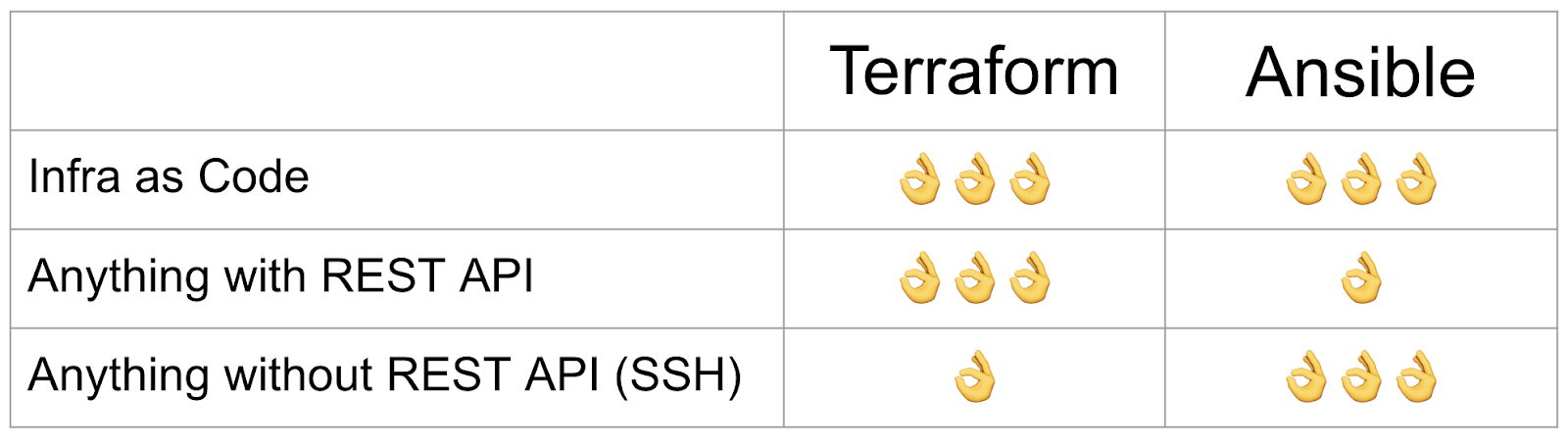
Some Use Cases for AAP and TFE Integration examples :
- Dynamic Data and Configuration:
- Configuring operating systems or application environments.
- Adjusting database configurations, logical files, or connection strings.
- Compliance at Launch:
- Enforcing organizational policies directly via Ansible playbooks.
- Hybrid Environments:
- Managing environments with components that require both API-based and SSH-based interactions.
This integration addresses critical challenges such as drift management, state file corruption, and performance bottlenecks in CI/CD workflows.
Integration Methods: AAP Provider or Run Tasks
The integration between Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) and Terraform Enterprise (TFE) can be achieved using two main methods: the AAP Provider for Terraform or Terraform Run Tasks. Each method offers distinct advantages depending on the use case.
- AAP Provider for Terraform: This approach integrates Ansible into the Terraform workflow by leveraging playbooks. It enables the orchestration of infrastructure, dynamic inventory management, and the execution of Ansible jobs as part of a Terraform run. This tightly coupled approach is well-suited for scenarios where provisioning and configuration management need to be closely aligned.
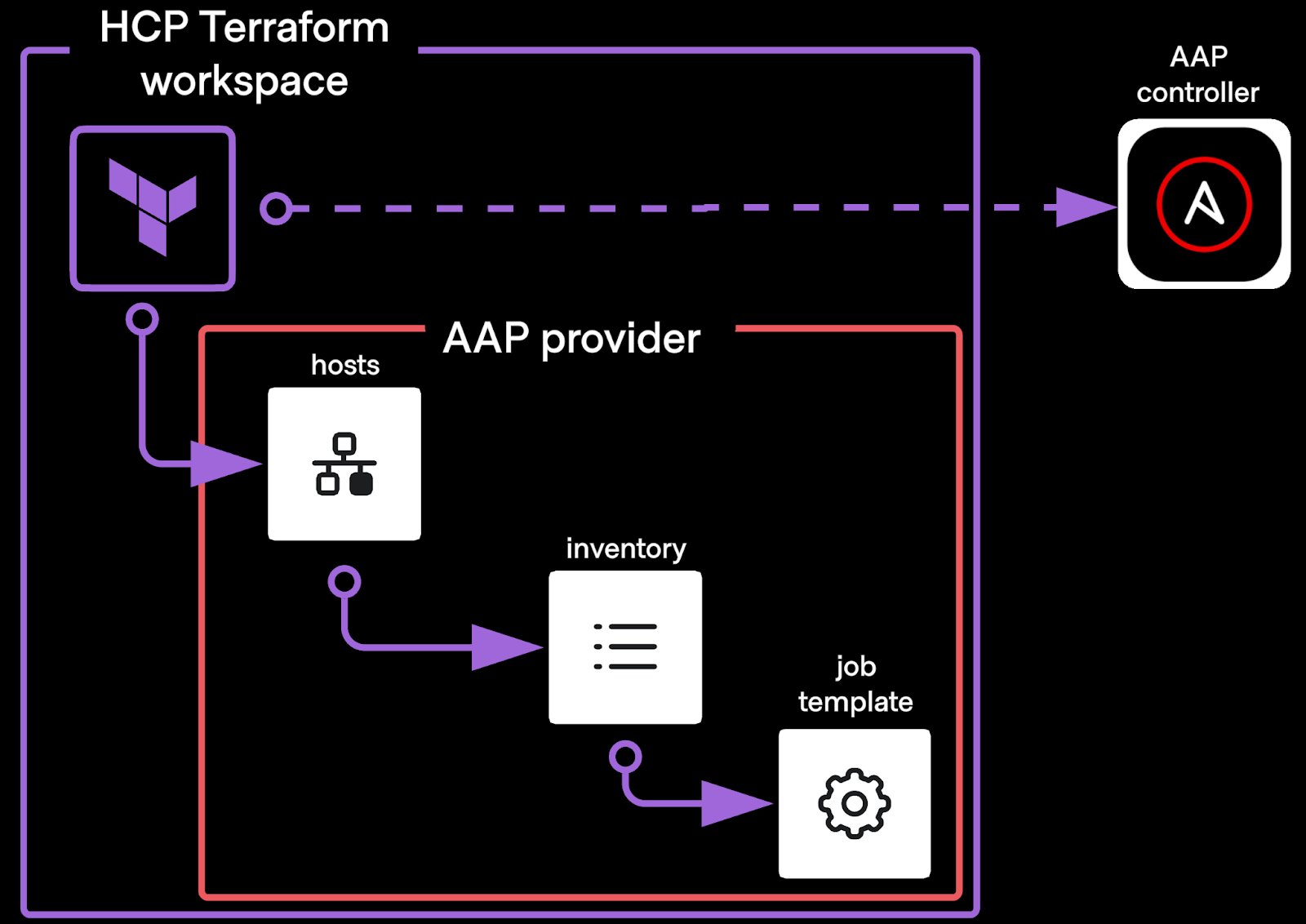
- Run Tasks: Terraform Enterprise’s run tasks allow Ansible Automation Platform workflows to be triggered at specific stages of a Terraform run. This loosely coupled method ensures modularity, enabling Terraform and Ansible to operate independently while maintaining a synchronized workflow. Keep in mind that inventory synchronisation needs to be developed there.
By selecting the appropriate method based on operational needs, organizations can maximize the benefits of both platforms, achieving efficient infrastructure automation while ensuring scalability and flexibility.
Inventory Management
A key element in the integration between Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) and Terraform Enterprise (TFE) is inventory management. Ansible Automation Platform relies on inventories to define which systems and resources it manages. When integrated with Terraform Enterprise, inventories can be dynamically updated during the provisioning process. This ensures that newly provisioned resources are immediately included within Ansible’s scope for configuration and compliance.
With dynamic inventory management:
- Automatic Registration: Terraform can automatically register newly provisioned infrastructure resources into Ansible’s inventory.
- Adaptive Management: AAP can dynamically adapt to changes in the environment without requiring manual updates, ensuring consistent configuration and management of all resources.
- Simplified Complexity: Hybrid or multi-cloud environments benefit from seamless synchronization between Terraform’s provisioning and Ansible’s configuration tasks.
This dynamic approach significantly reduces the risk of configuration drift and ensures that infrastructure changes are accurately reflected in automation workflows, enhancing both efficiency and reliability.
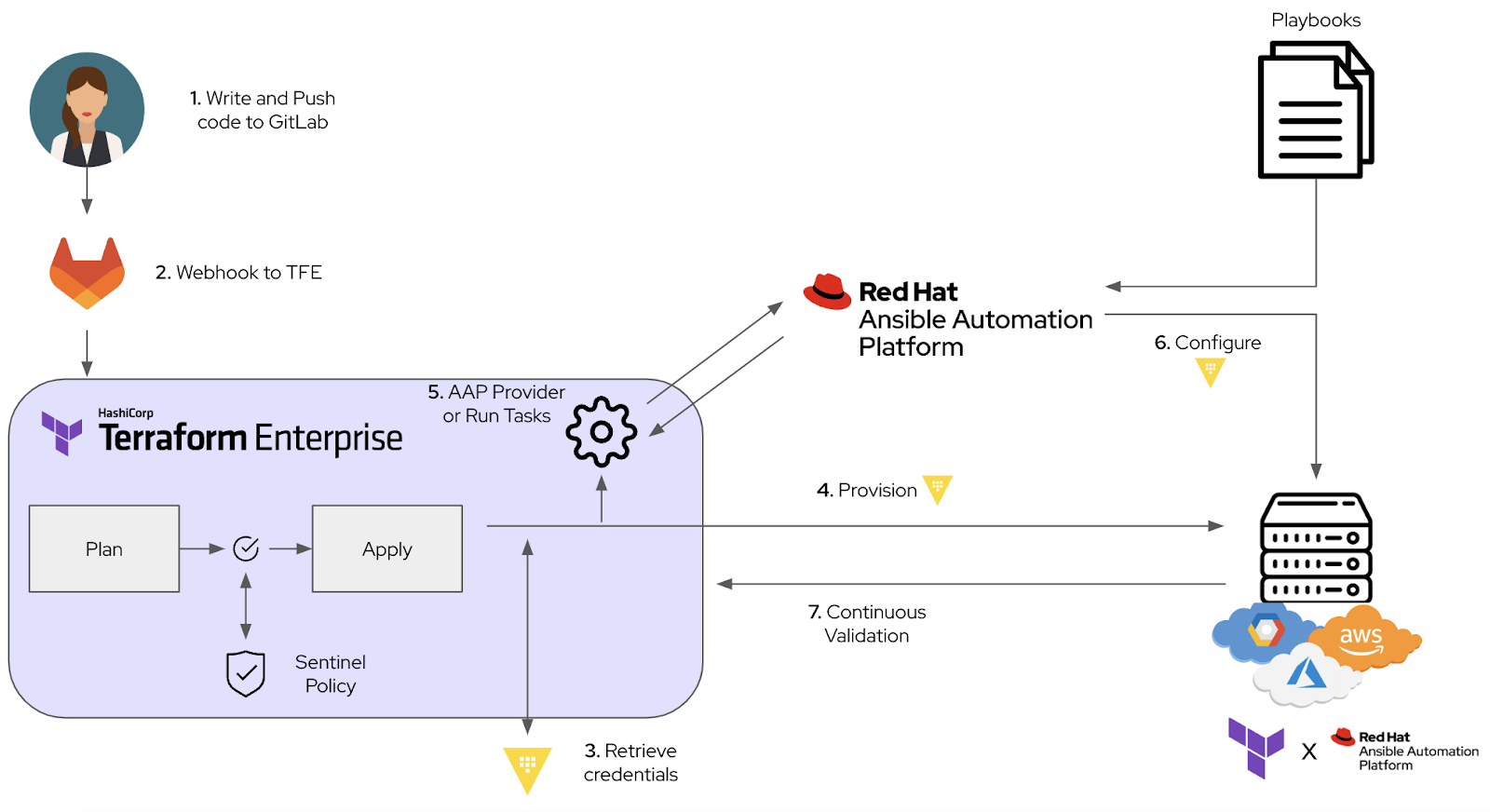
Architectural Overview :
The integration follows a GitLab → Terraform Enterprise → Ansible Automation Platform workflow:
- Code Submission: Developers push code to GitLab.
- Provisioning: Terraform Enterprise provisions infrastructure resources.
- Configuration: Ansible Automation Platform applies the necessary configurations and enforces compliance policies.
This approach ensures a consistent, traceable, and automated pipeline from infrastructure creation to configuration.
Steps details :
AAP Provider example :
Prerequisites: we need the playbook id to be able to call it from the AAP Provider (it can be obtained from the AAP UI url). Of course it can also be automated another way to retrieve the id from the playbook name.
https://registry.terraform.io/providers/ansible/aap/latest/docs/resources/job
provider "aap" {
host = var.aap_host_url
username = var.aap_username
password = var.aap_password
}
variable "aap_host_url" {
type = string
}
variable "aap_username" {
type = string
}
variable "aap_password" {
type = string
}
variable "job_template_id" {
type = number
description = "The job template id"
}
resource "aap_inventory" "my_inventory" {
name = "TFE_Apache-servers"
}
resource "aap_host" "create_host" {
inventory_id = aap_inventory.my_inventory.id
name = data.terraform_remote_state.aws-ec2.outputs.ec2_first_addr
}
resource "aap_job" "run_job_template" {
job_template_id = var.job_template_id
inventory_id = aap_inventory.my_inventory.id
extra_vars = <<EOT
{
"inventory": "${aap_inventory.my_inventory.name}"
}
EOT
}
Terraform AAP Provider lifecycle and inventory impact :
Create Phase
When Terraform provisions new infrastructure (e.g., VMs, containers, networks), the Terraform Provider for AAP updates the AAP inventory. This means that as soon as new resources are provisioned, the AAP inventory is automatically updated to include these new resources. This dynamic inventory management ensures that Ansible can immediately start managing and configuring the newly provisioned resources.
Destroy Phase
When Terraform destroys resources, the Terraform Provider for AAP updates the AAP inventory to remove the corresponding entries for the destroyed resources. This ensures that Ansible no longer attempts to manage or interact with resources that no longer exist, maintaining the accuracy and relevance of the inventory.
Dynamic Inventory Management
By integrating Terraform with the Ansible Automation Platform, you can create a dynamic inventory management system. This system automatically updates the inventory based on the current state of your infrastructure, as managed by Terraform. This is particularly useful in environments where infrastructure changes frequently, as it reduces the need for manual updates to the inventory.
Automation Workflow
Combining Terraform and Ansible allows for a seamless automation workflow. Terraform handles the provisioning and de-provisioning of infrastructure, while Ansible takes care of configuration management and application deployment. This integration ensures that your infrastructure and applications are always in sync, reducing the risk of configuration drift and improving overall efficiency.
Example Workflow :
- Provision Infrastructure: Terraform provisions new resources and updates the AAP inventory.
- Update Inventory: Ansible reads the updated AAP inventory and is ready to manage the new resources.
- Run Playbooks: Ansible runs playbooks to configure and deploy applications on the newly provisioned resources.
- Destroy Infrastructure: Terraform destroys resources and updates the AAP inventory.
- Remove Inventory Entries: Ansible removes the corresponding entries from its inventory.
This lifecycle ensures that Ansible always has an accurate view of the current state of your infrastructure, enabling efficient and reliable automation.
Take Aways :
Combining Terraform Enterprise and Ansible Automation Platform offers organizations a powerful, cohesive solution for managing infrastructure in complex, multi-cloud environments. This integration provides scalability, security, and efficiency, enabling teams to accelerate delivery while minimizing risk.
Sources :
AAP Terraform provider: https://github.com/ansible/terraform-provider-aap (warning : the Terraform AAP Provider for AAP 2.5 is not yet released)
Github Demo: https://github.com/Sokren/aap-tfc
Authors
This blog post was co-written with my friends from HashiCorp Rémi Salandre, Çetin Ardal, and from Red Hat David Jakubowicz
Linkedin :
- Rémi Salandre - HashiCorp
- Çetin ARDAL - HashiCorp
- David Jakubowicz - Red Hat
- Frédéric Klein - Red Hat